Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, affecting millions of people each year. It can develop on any part of the skin, making it crucial to be aware of the risks, signs, and preventive measures.
Understanding Skin Cancer
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably. The three main types of skin cancer are:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
- The most common form of skin cancer.
- Develops in the basal cells, which are found at the bottom of the epidermis (outer skin layer).
- Usually appears as a flesh-colored, pearl-like bump or a pinkish patch of skin.
- Commonly occurs on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, and arms.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
- The second most common form of skin cancer.
- Develops in the squamous cells, which make up most of the skin’s upper layers.
- Often appears as a red, firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then reopens.
- Typically found on sun-exposed areas but can develop anywhere on the body.
- Melanoma:
- The most dangerous form of skin cancer.
- Develops in melanocytes, the cells that produce the pigment melanin.
- Can appear as a new mole or a change in an existing mole (size, shape, color, or feel).
- Melanomas can develop anywhere on the body, even on areas not exposed to the sun.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing skin cancer, including:
- UV Radiation Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Fair Skin: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are more susceptible.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer increases the risk.
- Moles: Having a large number of moles or atypical moles.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions or medications that suppress the immune system.
- Age: The risk increases with age, though skin cancer can develop at any age.
Preventing Skin Cancer
Protecting your skin from UV radiation is the most effective way to reduce your risk of skin cancer. Here are some key prevention tips:
- Use Sunscreen
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin.
- Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
- Use sunscreen even on cloudy days and during the winter.
- Seek Shade
- Stay in the shade, especially during peak sun intensity hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use umbrellas, canopies, or other forms of shade when spending extended periods outdoors.
- Wear Protective Clothing
- Cover up with long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and wide-brimmed hats.
- Opt for clothing made from tightly woven fabrics or those labeled with a UV protection factor (UPF).
- Avoid Tanning Beds
- Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Embrace your natural skin tone and avoid artificial tanning.
- Wear Sunglasses
- Protect your eyes from UV radiation with sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays.
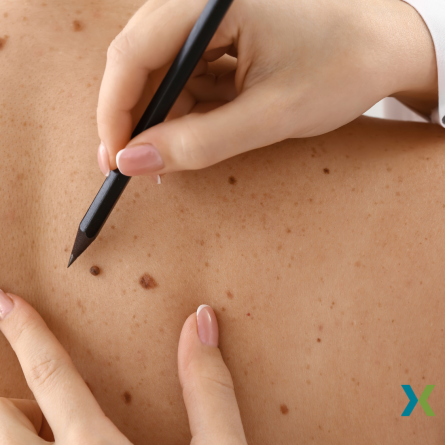
- Perform Regular Skin Checks
- Conduct monthly self-examinations to check for any new or changing moles, freckles, or spots.
- Use a mirror or ask a family member to help check hard-to-see areas.
Recognizing the Signs of Skin Cancer
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment of skin cancer. Be aware of the following warning signs:
- New Growths or Sores: Look for new growths, spots, or sores that don’t heal within a few weeks.
- Changes in Moles: Monitor existing moles for changes in size, shape, color, or texture.
- Unusual Skin Changes: Pay attention to any skin changes that seem out of the ordinary.
The ABCDEs of Melanoma:
- A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other half.
- B – Border: The edges are irregular, ragged, or blurred.
- C – Color: The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, or other colors.
- D – Diameter: The spot is larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- E – Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any unusual skin changes or have concerns about your skin, it’s important to seek medical advice. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
- Schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist.
- Visit a healthcare provider if you notice any of the ABCDEs of melanoma or other concerning changes.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious but preventable condition. By practicing sun safety, performing regular skin checks, and being aware of the signs and risk factors, you can protect yourself and your family.
![NL Wordmark [Gradient] NL Wordmark [Gradient]](https://www.nextlevelurgentcare.com/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/NL-Wordmark-Gradient-7fm1iv6f0zylwqrxpy8kifrnrzsluqzzzofvqvs6smo.png)